This page is about highlighting words (headwords or collocations), typically in examples or definitions. In this entry, the headword effervescent and the typical collocation personality are highlighted in the example sentence.
This page explains how to:
- set up your dictionary for highlighting
- insert a highlight
- delete a highlight
The highlighting may be required for purely aesthetical reasons and practicality but it can also be functional. For example, the highlighted collocation may link to the entry for personality. The formatting and behaviour of these highlights depends on the environment where the dictionary will be presented. If the dictionary is published in Lexonomy, the behaviour of the highlights can be set in the element configuration.
How does highlighting work?
Highlighting does not involve changing the format of the text. Instead, Lexonomy will mark the text as highlighted by inserting a child element. The highlights in this example are encoded in the dictionary data like this:
The fonts, sizes, colours and layout to be used when viewing the entry in Lexonomy are set in the dictionary configuration. They are not part of the raw dictionary data.
The colours in the structured editing mode are assigned automatically for practicality. The same elements use the same colour. To set the design of your dictionary when displaying in the Lexonomy viewer, use the dictionary configuration.
Links and tooltips
The highlights can also be converted to clickable links pointing to other dictionary entries or to pages on the web. Tooltips can also be displayed on mouseover. To learn to apply links and tooltips on highlights, refer to this page.
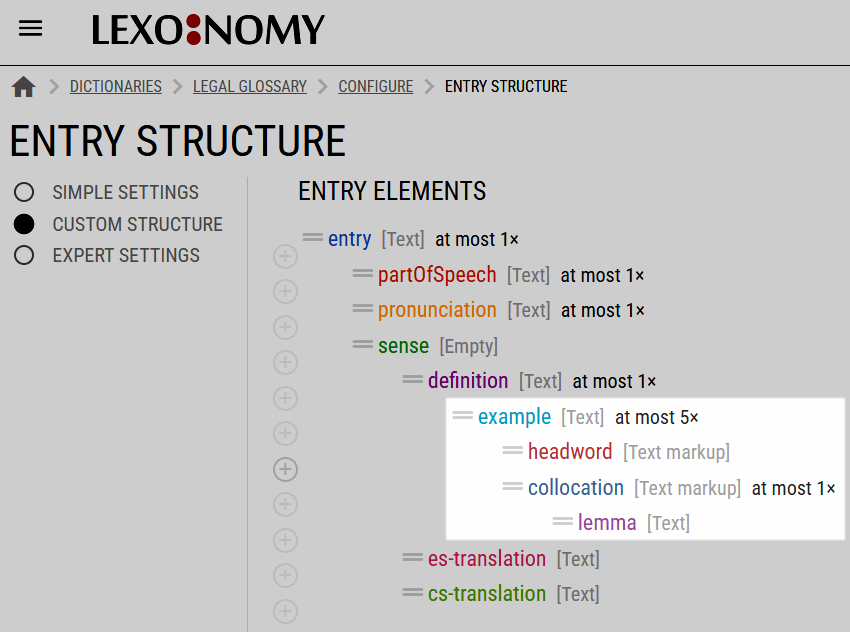
Preparing the entry structure
Highlighting is only possible if the entry structure defines the required child element(s). The child element must be type Text markup.
In this example, the highlighting is enabled for the example element. Two types of information can be highlighted: headword and collocation. While the headword can be highlighted more than once (in case it appears more than once in the example), only one collocation can be highlighted.
When a collocation is highlighted and it is not in the base form, the editor can insert a lemma of the collocation. This is useful if the highlight should link to the entry for the collocation.
Technical limitation
There is no limit to the types of highlight elements. In the example above, example has two types of highlight elements: headword and collocation. These highlight elements can have children – lemma in the example above or url in the example below. However, they are not allowed to have their own children. It is not possible to insert an element dependent on lemma or on url.
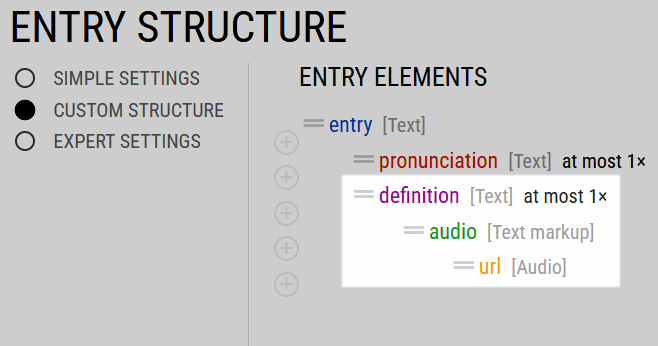
In this example, the highlighting is enabled for the definition element. The highlight indicates which words should be linked to an audio recordings. The url of the recording is a child element of the highlight.
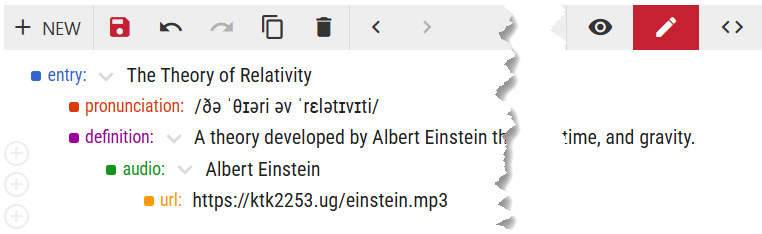
This is what the data look like in the entry editor.
The audio and url elements are dependent on definition. This means that the text Albert Einstein in the definition should be highlighted and is associated with the url. How exactly this information will be displayed to the user depends on the interface in which the dictionary is presented. If it is presented in Lexonomy, the styling and behaviour can be set in the dictionary configuration.
The element can by styled as required.
The fonts, sizes, colours and layout to be used when viewing the entry in Lexonomy are set in the dictionary configuration. They are not part of the raw dictionary data.
Inserting highlights
After you have configured the element for highlighting, you can start inserting the highlights:
- select the element with the keyboard or click on it
- select the text to be highlighted
- click on one of the highlight type buttons
- hit Enter to save the element
the text will not become bold or coloured but you will see a new highlight element - press Ctrl+S to save the whole entry
Only child entries which are type Text markup will be shown as the highlight type buttons.
When you switch to the visual mode, you can see how the element will be highlighted when publishing the dictionary in Lexonomy. You can change this in configuration.
Child elements
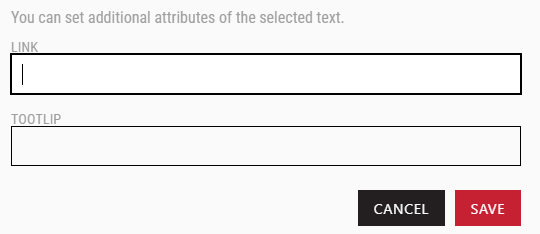
If the highlight has child elements, for example a text of a tooltip or URL, or any other child elements, a popup will appear allowing you to input this information.
Delete a highlight
Delete the highlight element.
Troubleshooting
There are no highlighting buttons.
If no highlighting buttons are shown when you are editing the element, the element is not properly set up for highlighting. Check that the entry structure:
- contains a child element
- the child element is set to type Text markup
The highlighted element is not in bold / is not in red….
The actual styling of the highlight is only visible in the visual mode of the editor. By default, the highlight is not styled. You need to tell Lexonomy, how the highlighted element should be presented to the user. This is done in CONFIGURATION – FORMATTING.